dict.cc
⇄
⇄
Werbung
| NOUN | a nerve cell | nerve cells | |
| SYNO | nerve cell | neuron |
Übersetzung für 'nerve cell' von Englisch nach Deutsch
- nerve cell
- Nervenzelle {f}biol.
- nerve cell bodies
- Nervenzellkörper {pl}biol.
Wurzelzellen {pl} [Nervenzellkörper]biol. - Werbung
- nerve cell membrane
- Nervenzellmembran {f}biol.
- nerve cell type
- Nervenzelltyp {m}biol.
- beta cell <β-cell, B cell>
- Betazelle {f} <β-Zelle, B-Zelle>biol.
- natural killer T cell <NKT cell>
- natürliche Killer-T-Zelle {f} <NKT-Zelle>med.
- Chinese hamster ovary cell <CHO cell>
- Chinesische Hamster-Ovarienzelle {f} [selten] [CHO-Zelle]biol.
Chinese-Hamster-Ovary-Zelle {f} [selten] [CHO-Zelle]med. - amorphous silicon cell <a-Si cell>
- amorphe Siliziumzelle {f} <a-Si-Zelle>chem.phys.
- human embryonic kidney cell <HEK cell>
- HEK-Zelle {f}biol.
- differential pressure cell <d/p cell>
- Differenzdruck-Messzelle {f}tech.
- lupus erythematosus cell <LE cell>
- Lupus-erythematodes-Zelle {f} <LE-Zelle>med.
- natural killer cell <NK cell>
- natürliche Killerzelle {f} <NK-Zelle>med.
- enterochromaffin cell <ECC, EC cell>
- enterochromaffine Zelle {f} <EC-Zelle>biol.
- progenitor cell <PG cell>
- Vorläuferzelle {f}biol.
Progenitorzelle {f} <PG-Zelle>biol.
determinierte Stammzelle {f} [selten] [Progenitorzelle]biol. - cell-to-cell communication
- Zell-zu-Zell-Kommunikation {f}biol.
- cell-cell recognition
- Zell-Zell-Erkennung {f}biol.
- embryonic stem cell <ES, ES cell>
- embryonale Stammzelle {f} <ES, ES-Zelle>acad.biotech.med.
- to nerve
- nerven [ugs.]
- proboscis nerve
- Proboscisnerv {m}zool.
- antennal nerve
- Antennennerv {m}zool.
- palp nerve
- Palpennerv {m}zool.
Anwendungsbeispiele Englisch
weitere Beispiele ...
- He was a proponent of polarization of nerve cell function and his student, Rafael Lorente de Nó, would continue this study of input-output systems into cable theory and some of the earliest circuit analysis of neural structures.
- It inhibits the firing of action potentials in neurons by binding to the voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cell membranes and blocking the passage of sodium ions (responsible for the rising phase of an action potential) into the neuron.
- Conopeptides are also being looked at as anti-epileptic agents and to help stop nerve-cell death after a stroke or head injury.
- A pseudoganglion looks like a ganglion, but only has nerve fibers and has no nerve cell bodies.
- The patients can present with symptoms indicating spinal cord involvement such as (paralysis of arms and legs, numbness and loss of sensation and sphincter dysfunction), and pathological examination reveals disseminated nerve cell death in the spinal cord.
- Huxley, Alan Hodgkin and John Eccles jointly won the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the ionic mechanisms involved in excitation and inhibition in the peripheral and central portions of the nerve cell membrane".
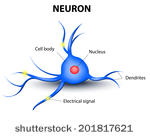
- Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον "déndron", "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project.
- It is thought that the reason for this is that a certain minimum number of ions must be driven across a nerve cell's membrane by the imposed voltage to trigger the nerve cell to depolarize and transmit an impulse.
- White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons.
- An electrical stimulation can artificially elicit this action potential by changing the electric potential across a nerve cell membrane (this also includes the nerve axon) by inducing electrical charge in the immediate vicinity of the outer membrane of the cell.
- An autonomic ganglion is a cluster of nerve cell bodies (a ganglion) in the autonomic nervous system. The two types are the sympathetic ganglion and the parasympathetic ganglion.
- Inflammation associated with nerve cell destruction often alters the color and appearance of the gray matter in the spinal column, causing it to appear reddish and swollen.
- The nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell—the neuron (sometimes called "neurone" or "nerve cell").
- A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via synapses - specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap.
- In 1907 the zoologist Ross Granville Harrison demonstrated the growth of frog nerve cell processes in a medium of clotted lymph. It is made up of lymph nodes and vessels.
- Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon.
- The transfer of potassium ions across nerve cell membranes is necessary for normal nerve transmission; potassium deficiency and excess can each result in numerous signs and symptoms, including an abnormal heart rhythm and various electrocardiographic abnormalities.
Werbung